reason
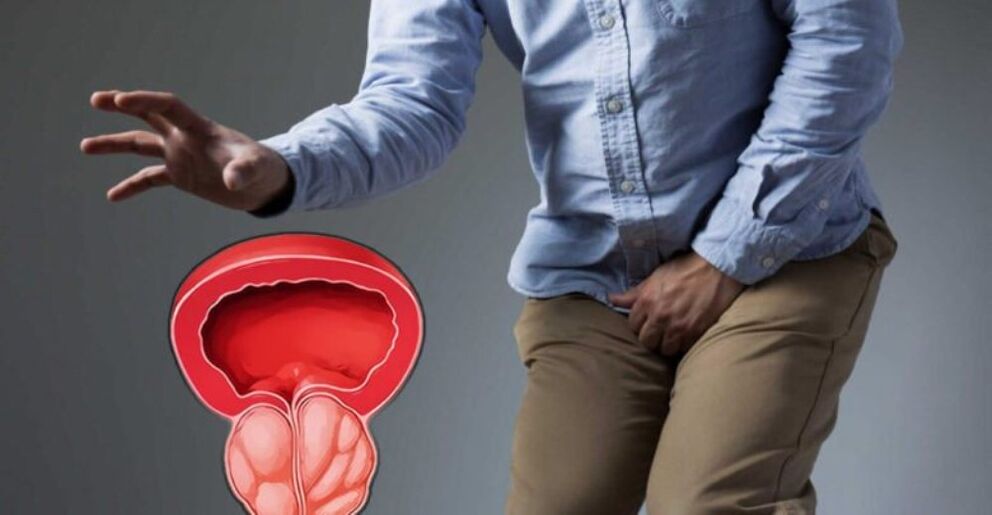
What causes prostatitis
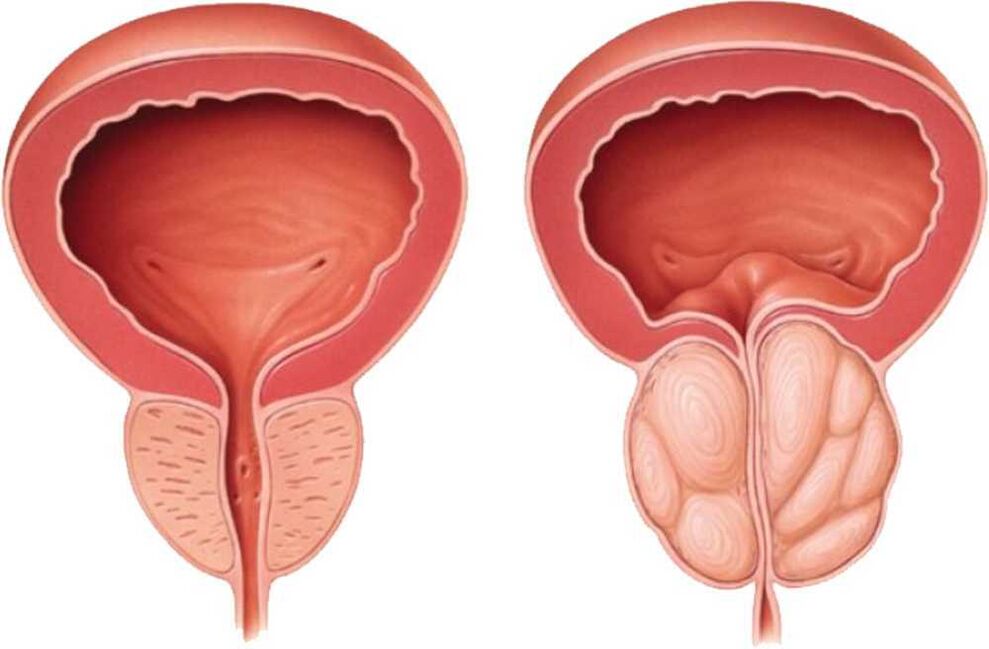
Doctor's opinion: Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the prostate that can lead to a variety of unpleasant symptoms, such as genitourinary pain, urinary tract problems, and general discomfort. Doctors recommend seeking help at the first signs of the disease, as inappropriate treatment or lack of treatment can lead to chronic prostatitis and complications. In order to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the best treatment, you need to contact a urologist who will perform the necessary tests and choose an appropriate treatment. It is important to remember that prostatitis requires a comprehensive treatment approach, including medication, physical therapy, and regular monitoring by a specialist.
symptom
Diagnosis of prostatitis
interesting facts
- Prostatitis can affect men of any age:Although prostatitis is more common in men over 50, even younger men can develop it.
- There are many causes of prostatitis:The most common causes include bacterial infection, inflammation, and prostate duct obstruction. In some cases, the cause may be unknown.
- Prostatitis can have a variety of symptoms:These symptoms range from mild discomfort to severe pain when urinating, fever, and chills. Symptoms usually depend on the type of prostatitis and its severity.